The morphology of a flower, or its form and structure, can be considered in two parts: the vegetative part, consisting of non-reproductive structures such as petals; and the reproductive or sexual parts. A stereotypical flower is made up of four kinds of structures attached to the tip of a short stalk or axis, called a receptacle. Each of these parts or floral organs is arranged in a spiral called a whorl. The four main whorls (starting from the base of the flower or lowest node and working upwards) are the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium. Together the calyx and corolla make up the non-reproductive part of the flower called the perianth, and in some cases may not be differentiated. If this is the case, then they are described as tepals.
Most flowering plants depend on animals, such as bees, moths, and butterflies, to transfer their pollen between different flowers, and have evolved to attract these pollinators by various strategies, including brightly colored, conspicuous petals, attractive scents, and the production of nectar, a food source for pollinators.[1] In this way, many flowering plants have co-evolved with pollinators to be mutually dependent on services they provide to one another—in the plant's case, a means of reproduction; in the pollinator's case, a source of food.
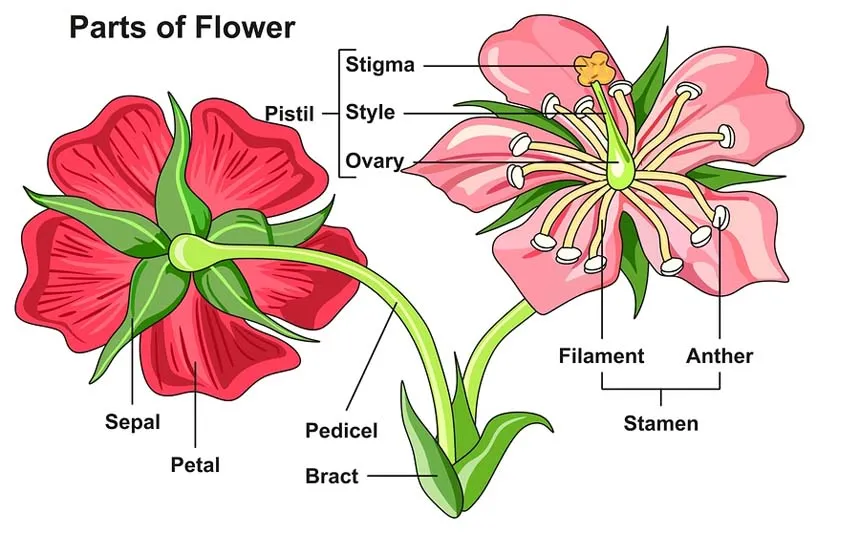
Although this arrangement is considered "typical", plant species show a wide variation in floral structure. The four main parts of a flower are generally defined by their positions on the receptacle and not by their function. Many flowers lack some parts or parts may be modified into other functions or look like what is typically another part. In some families, such as the grasses, the petals are greatly reduced; in many species, the sepals are colorful and petal-like. Other flowers have modified stamens that are petal-like; the double flowers of Peonies and Roses are mostly petaloid stamens.
Many flowers have symmetry. When the perianth is bisected through the central axis from any point and symmetrical halves are produced, the flower is said to be actinomorphic or regular. This is an example of radial symmetry. When flowers are bisected and produce only one line that produces symmetrical halves, the flower is said to be irregular or zygomorphic. If, in rare cases, they have no symmetry at all they are called asymmetric.
Flowers may be directly attached to the plant at their base (sessile—the supporting stalk or stem is highly reduced or absent). The stem or stalk subtending a flower, or an inflorescence of flowers, is called a peduncle. If a peduncle supports more than one flower, the stems connecting each flower to the main axis are called pedicels. The apex of a flowering stem forms a terminal swelling which is called the torus or receptacle.
In the majority of species, individual flowers have both pistils and stamens. These flowers are described by botanists as being perfect, bisexual, or hermaphrodite. In some species of plants, the flowers are imperfect or unisexual: having only either male (stamens) or female (pistil) parts. If unisexual male and female flowers appear on the same plant, the species is called monoecious.,However if an individual plant is either female or male, the species is called dioecious. Many flowers have nectaries, which are glands that produce a sugary fluid used to attract pollinators. They are not considered as an organ on their own.
