
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants (fuel/oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder. The inception of gunpowder rockets in warfare can be credited to the ancient Chinese, and in the 13th century, the Mongols played a pivotal role in facilitating their westward adoption.
All rockets used some form of solid or powdered propellant until the 20th century, when liquid-propellant rockets offered more efficient and controllable alternatives. Because of their simplicity and reliability, solid rockets are still used today in military armaments worldwide, model rockets, solid rocket boosters and on larger applications.
Since solid-fuel rockets can remain in storage for an extended period without much propellant degradation, and since they almost always launch reliably, they have been frequently used in military applications such as missiles. The lower performance of solid propellants (as compared to liquids) does not favor their use as primary propulsion in modern medium-to-large launch vehicles customarily used for commercial satellites and major space probes. Solids are, however, frequently used as strap-on boosters to increase payload capacity or as spin-stabilized add-on upper stages when higher-than-normal velocities are required. Solid rockets are used as light launch vehicles for low Earth orbit (LEO) payloads under 2 tons or escape payloads up to 500 kilograms (1,100 lb).
Most commercial motors come the like ether of these
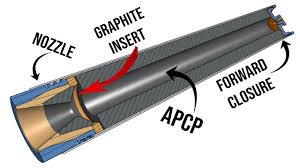

A simple solid rocket motor consists of a casing, nozzle, grain (propellant charge), and igniter.
The solid grain mass burns in a predictable fashion to produce exhaust gases, the flow of which is described by Taylor–Culick flow. The nozzle dimensions are calculated to maintain a design chamber pressure, while producing thrust from the exhaust gases.
Once ignited, a simple solid rocket motor cannot be shut off, as it contains all the ingredients necessary for combustion within the chamber in which they are burned. More advanced solid rocket motors can be throttled, or extinguished and re-ignited, by control of the nozzle geometry or through the use of vent ports. Further, pulsed rocket motors that burn in segments, and that can be ignited upon command are available.
Here is a experimental rocket launch