UTF-8
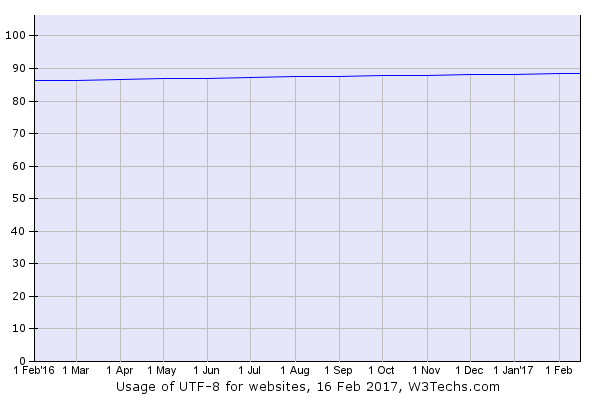
UTF stand for Unicode Transformation Format, Unicode is able to represent all characters in every language. Unicode has around 1,114,112 different characters. ASCII only has 128 possible patterns and only in one language it isn't very helpful for people in different countries. Unicode covers all countries and has millions of characters for example Japan, China. The diagram below shows that UTF-8 is being used in nearly 90% of websites around the world and is slowly increasing. It is used in nearly every website because mainly UTF-8 can support many languages and can accommodate pages and forms in any mixture of languages, it also eliminates the need for server-side logic to individually determine the character encoding for the page served or each incoming form submission.
To show how UTF-8 works I have chosen a Chinese character 平 and using its binary number 11100101 10111001 10110011 in the table below we can match the pattern of the binary numbers. For example the binary numbers match the same first four bits 1110 and the second bits 10 of pattern 16. The x's represent the left over numbers in the pattern, so by using the pattern 16 the binary sequence will be coded into the character I choose 平. 7 or fewer bits: 0xxxxxxx 11 or fewer bits: 110xxxxx 10xxxxxx 16 or fewer bits: 1110xxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx 21 or fewer bits: 11110xxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx Character Decimal Binary 平 24179 11100101 10111001 10110011 As shown above the character has the number of 24179 and a binary of 11100101 10111001 10110011 this binary will use 16 bits, I know this by looking at the patterns on the table above I can tell that this binary code has the same pattern as pattern 16.
Representation Variable or Fixed Bits per Character Real world Usage ASCII Fixed Length 8 bits No longer widely used UTF-8 Variable Length 8, 16, 24, or 32 bits Very widely used UTF-16 Variable Length 16 or 32 bits Widely used UTF-32 Fixed Length 32 bits Rarely used
The table above shows if the coding is a fixed or flexible/variable length, as you can see UTF-8 and UTF-16 are both flexible lengths and are more widely used then ASCII and UTF-32 which are fixed lengths. Fixed length means that they don't have another option for example UTF-32 only has 32 bits and cannot be changed, UTF-16 has between 16 and 32 bits which makes it flexible, UTF-8 has between 8, 16, 24 and 32 bits which also makes it flexible. UTF-8 is better for English text and UTF-16 is better for Asian text.
